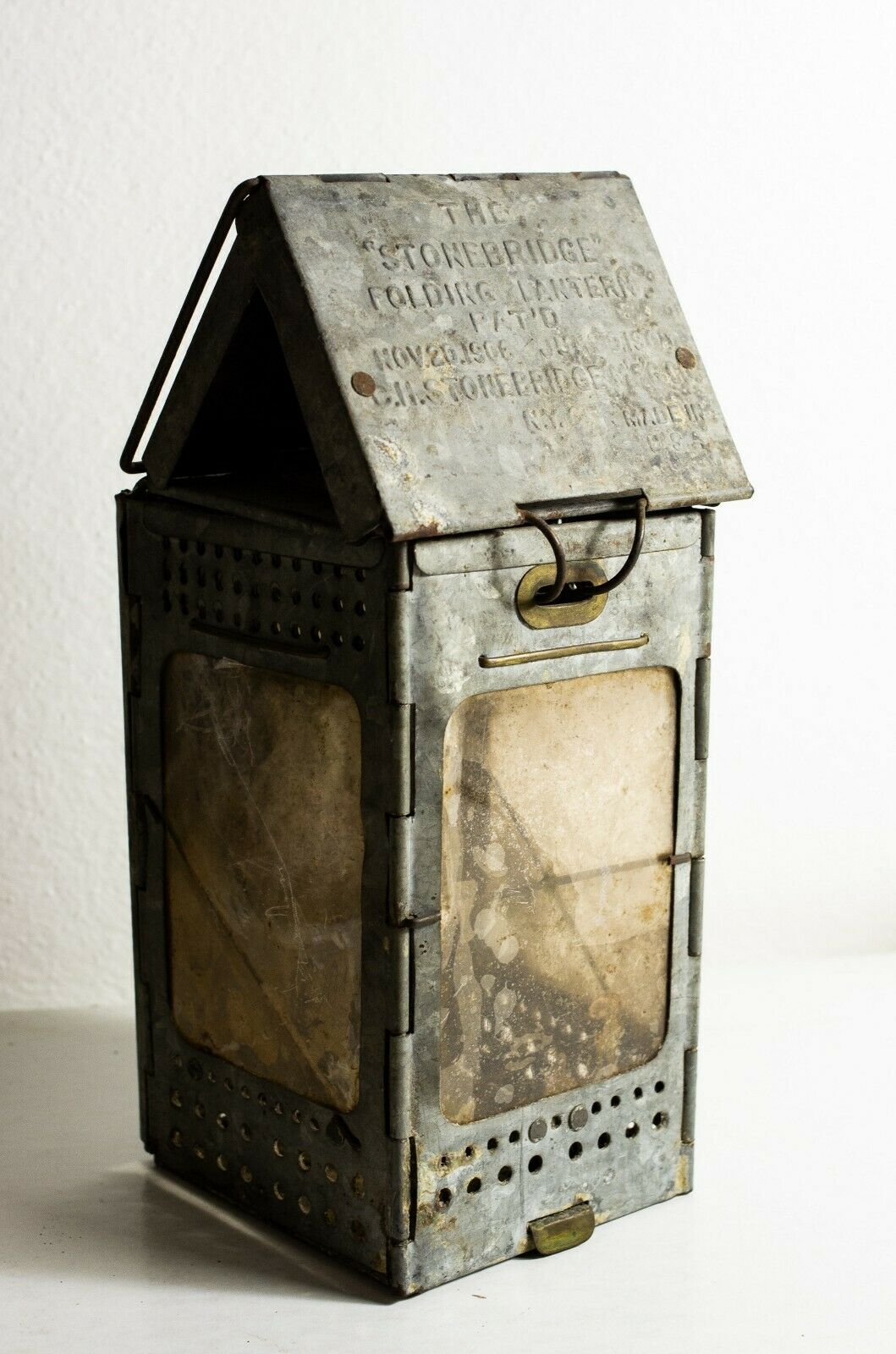
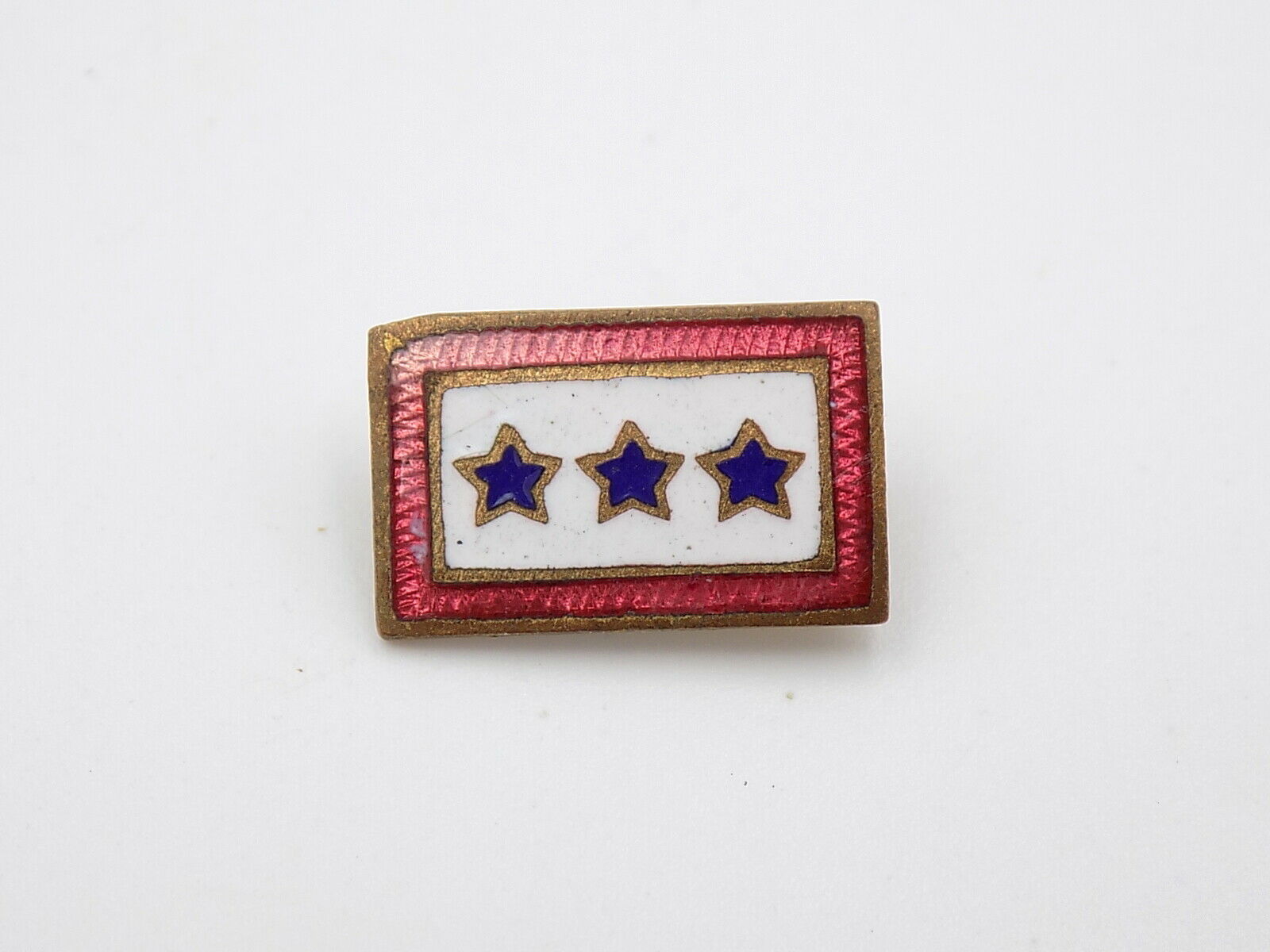
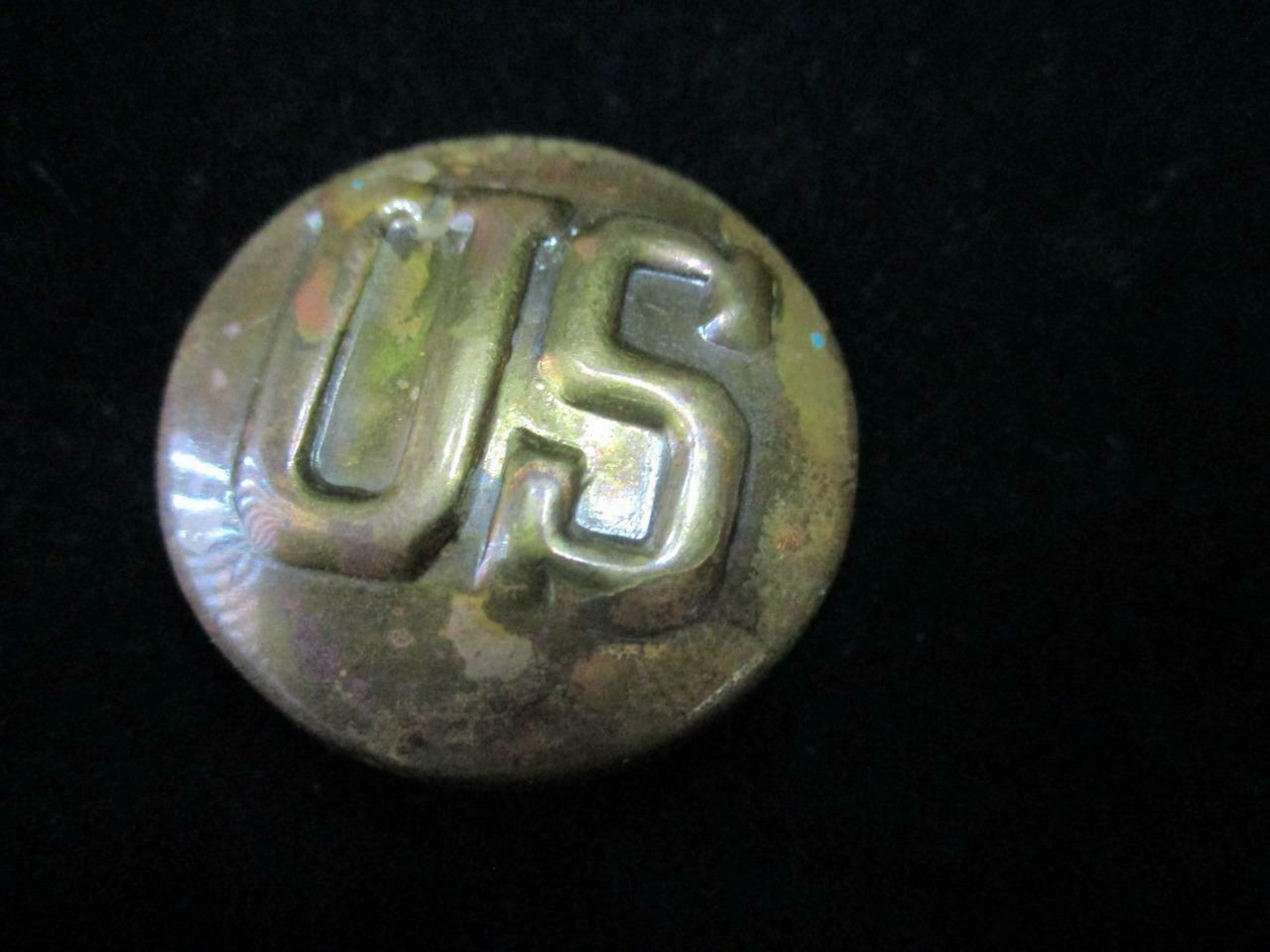-40%
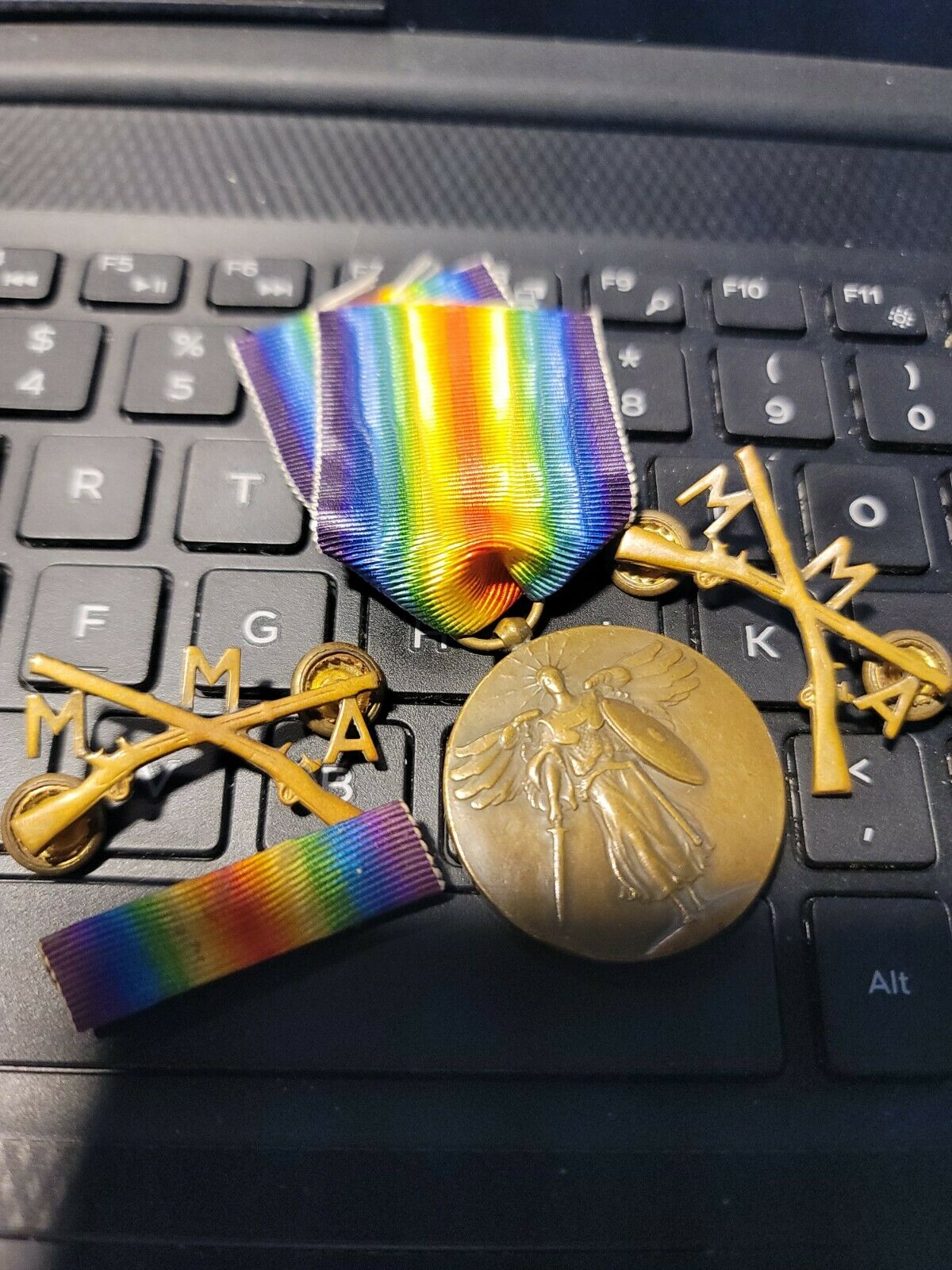
WW1 VICTORY MEDAL WITH PAIR OF OFFICERS COLLAR DEVICE+ RIBBON
$ 52.79
- Description
- Size Guide
Description
PLEASE FOLLOW OUR E BAY STORESEE ALL PICS
SALE
SEE OUR STORE
PLEASE READ WHOLE ADD
American Expeditionary Forces
From Wikipedia, the free encyclopedia
Jump to navigation
Jump to search
American Expeditionary Forces
Officers of the AEF and the Baker Mission,
c.
1918
Active
1917–1920
Disbanded
August 31, 1920
Country
United States
Branch
United States Army
General Headquarters
Chaumont
,
France
Engagements
World War I
Western Front
Battle of Cambrai
German spring offensive
Battle of Cantigny
Battle of Belleau Wood
Second Battle of the Marne
Battle of Château-Thierry
Hundred Days Offensive
Second Battle of the Somme
Battle of St Quentin Canal
Battle of Saint-Mihiel
Meuse-Argonne Offensive
Italian Front
Battle of Vittorio Veneto
Commanders
Commander in Chief
General of the Armies
John J. Pershing
Commander of U.S. Naval Forces operating in European waters
Vice Admiral
William Sims
Chief of the
Army Air Service
Major General
Mason Patrick
The
American Expeditionary Forces
(
A.E.F.
or
AEF
) was a formation of the
United States Army
on the
Western Front
of
World War I
. The AEF was established on July 5, 1917, in
France
under the command of Gen.
John J. Pershing
. It fought alongside
French Army
,
British Army
,
Canadian Army
, and
Australian Army
units against the
Imperial German Army
. A minority of the AEF troops also fought alongside
Italian Army
units in that same year against the
Austro-Hungarian Army
. The AEF helped the French Army on the Western Front during the
Aisne Offensive
(at the
Battle of Château-Thierry
and
Battle of Belleau Wood
) in the summer of 1918, and fought its major actions in the
Battle of Saint-Mihiel
and the
Meuse-Argonne Offensive
in the latter part of 1918.
Formation
[
edit
]
Further information:
American Expeditionary Forces on the Western Front (World War I) order of battle
American Expeditionary Forces Commander in Chief, Gen.
John J. Pershing
, 1917
President Woodrow Wilson
initially planned to give command of the AEF to Gen.
Frederick Funston
, but after Funston's sudden death, Wilson appointed Major General
John J. Pershing
in May 1917, and Pershing remained in command for the entire war. Pershing insisted that American soldiers be well-trained before going to Europe. As a result, few troops arrived before January 1918. In addition, Pershing insisted that the American force would not be used merely to fill gaps in the French and British armies, and he resisted European efforts to have U.S. troops deployed as individual replacements in decimated
Allied units
. This approach was not always well received by the western Allied leaders who distrusted the potential of an army lacking experience in large-scale warfare.
[1]
In addition, the British government tried to use its spare shipping as leverage to bring US soldiers under British operational control.
Column of American troops passing Buckingham Palace, London, 1917.
By June 1917, only 14,000 American soldiers had arrived in France, and the AEF had only a minor participation at the front through late October 1917, but by May 1918 over one million American troops were stationed in France, though only half of them made it to the front lines.
[2]
Since the
transport ships
needed to bring American troops to Europe were scarce at the beginning, the U.S. Army pressed into service passenger liners, seized German ships, and borrowed Allied ships to transport American soldiers from ports in
New York City
,
New Jersey
, and
Virginia
. The mobilization effort taxed the American military to the limit and required new organizational strategies and command structures to transport great numbers of troops and supplies quickly and efficiently. The French harbors of
Bordeaux
,
La Pallice
,
Saint Nazaire
, and
Brest
became the entry points into the French railway system that brought the American troops and their supplies to the Western Front. American engineers in France also built 82 new ship berths, nearly 1,000 miles (1,600 km) of additional standard-gauge tracks, and over 100,000 miles (160,000 km) of telephone and telegraph lines.
[1]
The first American troops, who were often called "
Doughboys
," landed in Europe in June 1917. However the AEF did not participate at the front until October 21, 1917, when the
1st Division
fired the first American shell of the war toward German lines, although they participated only on a small scale. A group of regular soldiers and the first American division to arrive in France, entered the trenches near
Nancy, France
, in
Lorraine
.
[1]
With America's first convoy. The troop ships are
Henderson
,
Antilles
,
Momus
, and
Lenape
.
I Corps was officially activated in France, under AEF, from 15 January 1918. It include the 1st, 2nd, 26th, 32nd, 41st and 42nd Divisions. (4th Brigade, US Marine Corps, was included as part of 2nd Division.) II Corps was activated on 24 February,
[3]
by which time troop numbers justified it. Initially II Corps consisted of the 27th, 30th, 33rd, 78th and 80th Divisions.
In June 1918, many component infantry units from II Corps – commanded by Maj.-Gen.
George W. Read
– were attached to veteran
British Army
or
Australian Army
units. This served two purposes: familiarizing the Americans with actual battlefield conditions in France, and temporarily reinforcing the British Empire units that were often severely-depleted in numbers, after more than three years of fighting. In fact, the first major operation in World War I to involve US troops concerned individual infantry platoons of the 33rd Division, which were attached to battalions of the
Australian Corps
for the
Battle of Hamel
on the 4th of July. Their involvement was voluntary and occurred despite last-minute orders from AEF headquarters, that its troops should not take part in offensive operations led by non-US generals. Thus Hamel was historically significant as the first major offensive operation during the war to involve US infantry and the first occasion on which US units had fought alongside British Empire forces.
The AEF used French and British equipment. Particularly appreciated were the French
canon de 75 modèle 1897
, the
canon de 155 C modèle 1917 Schneider
, and the
canon de 155mm GPF
. American aviation units received the
SPAD XIII
and
Nieuport 28
fighters, and the U.S. Army tank corps used French
Renault FT
light tanks. Pershing established facilities in France to train new arrivals with their new weapons.
[4]
By the end of 1917, four divisions were deployed in a large training area near
Verdun
: the 1st Division, a regular army formation; the
26th Division
, a
National Guard
division; the
2nd Division
, a combination of regular troops and
U.S. Marines
; and the
42nd "Rainbow" Division
, a National Guard division made up of soldiers from nearly every state in the United States. The fifth division, the
41st Division
, was converted into a depot division near
Tours
.
Logistics
[
edit
]
Main article:
Services of Supply, American Expeditionary Forces
A. E. F. officer's identity card, 1918
Logistic operations were under the direction of Chicago banker
Charles G. Dawes
, with the rank first of colonel and then brigadier general. Dawes reported directly to Gen. Pershing. Dawes recommended in May 1918 that the allies set up a joint logistics planning board, which was approved by the Allies in the form of the
Military Board of Allied Supply
(MBAS), which coordinated logistics and transportation on the Western and Italian fronts.
[5]
Supporting the two million soldiers across the Atlantic Ocean was a massive logistical enterprise. In order to be successful, the Americans needed to create a coherent support structure with very little institutional knowledge. The AEF developed support network appropriate for the huge size of the American force. It rested upon the
Services of Supply
in the rear areas, with ports, railroads, depots, schools, maintenance facilities, bakeries, clothing repair shops (termed salvage), replacement depots, ice plants, and a wide variety of other activities.
The Services of Supply initiated support techniques that would last well into the Cold War including forward maintenance, field cooking, graves registration (mortuary affairs), host nation support, motor transport, and morale services. The work of the logisticians enabled the success of the AEF and contributed to the emergence of the American Army as a modern fighting force.
[6]
African Americans
[
edit
]
Officers of the
366th Infantry
, 1919
African Americans
were drafted on the same basis as
whites
and made up 13 percent of the draftees. By the end of the war, over 350,000 African-Americans had served in AEF units on the Western Front.
[7]
However, they were assigned to segregated units commanded by white officers. One fifth of the black soldiers sent to France saw combat, compared to two-thirds of the whites. They were three percent of AEF combat forces, and under two percent of battlefield fatalities.
[8]
"The mass of the colored drafted men cannot be used for combatant troops", said a General Staff report in 1918, and it recommended that "these colored drafted men be organized in reserve labor battalions." They handled unskilled labor tasks as
stevedores
in the Atlantic ports and common laborers at the camps and in the Services of the Rear in France.
[9]
The French, whose front-line troops were resisting combat duties to the point of mutiny, requested and received control of several regiments of black combat troops.
[10]
Kennedy reports "Units of the black
92nd Division
particularly suffered from poor preparation and the breakdown in command control. As the only black combat division, the 92nd Division entered the line with unique liabilities. It had been deliberately dispersed throughout several camps during its stateside training; some of its artillery units were summoned to France before they had completed their courses of instruction, and were never fully-equipped until after the Armistice; nearly all its senior white officers scorned the men under their command and repeatedly asked to be transferred. The black enlisted men were frequently diverted from their already attenuated training opportunities in France in the summer of 1918 and put to work as stevedores and common laborers."
[11]
The
369th
,
370th
,
371st
, and
372nd Infantry Regiments
(nominally the
93d Division
, but never consolidated as such) served with distinction under French command with French colonial units in front-line combat. The French did not harbor the same levels of disdain based on skin color and for many Americans of an African-American descent it was a liberating and refreshing experience.
[
citation needed
]
These African-American soldiers wore American uniforms, some dating from the time of the Union Army, with
French helmets
and were armed with French Model 1907/15
8mm Lebel
Berthier rifle
, and Fusil Mle 1907/15 manufactured by
Remington Arms
rather than the
M1903 Springfield
or
M1917 Enfield
rifles issued to most American soldiers.
[12]
One of the most distinguished units was the 369th Infantry Regiment, known as the
Harlem Hellfighters
. The 369th was on the front lines for six months, longer than any other African-American regiment in the war. One hundred seventy-one members of the 369th were awarded the
Legion of Merit
.
[13]
One member of the 369th,
Sergeant
Henry Johnson
, was awarded the
French
Croix de guerre
,
[14]
and posthumously the
Medal of Honor
.
[15]
Actions during World War I
[
edit
]
Further information:
Western Front (World War I)
Allies gain overwhelming superiority in front-line rifle strength as American soldiers arrive in the summer
[16]
At the beginning, during the spring of 1918, the four battle-ready U.S. divisions were deployed under French and British command to gain combat experience by defending relatively quiet sectors of their lines. After the first offensive action and American-led AEF victory on 28 May 1918 at the
Battle of Cantigny
,
[17]
by the
U.S. 1st Division
, and a similar local action by the
2nd Division
at
Belleau Wood
beginning 6 June, both while assigned under French Corps command, Pershing worked towards the deployment of an independent US field Army. The rest followed at an accelerating pace during the spring and summer of 1918. By June Americans were arriving in-theater at the rate of 10,000 a day; most of which entered training by British, Canadian and Australian battle-experienced officers and senior non-commissioned ranks. The training took a minimum of six weeks due to the inexperience of the servicemen.
The first offensive action by AEF units serving under non-American command was 1,000 men (four companies from the
33d Division
AEF), with the
Australian Corps
during the
Battle of Hamel
on 4 July 1918. (
Corporal
Thomas A. Pope
was awarded the
Medal of Honor
for this battle.) This battle took place under the overall command of the Australian Corps commander, Lt. Gen. Sir
John Monash
. The Allied force in this battle combined artillery, armor, infantry, and air support (
combined arms
), which served as a blueprint for all subsequent Allied attacks, using "
tanks
".
[18]
Army field hospital in France, 1918
U.S. Army and
Marine Corps
troops played a key role in helping stop the German thrust towards Paris, during the
Second Battle of the Marne
in June 1918 (at the
Battle of Château-Thierry (1918)
and the
Battle of Belleau Wood
). The first major and distinctly American offensive was the reduction of the Saint Mihiel salient during September 1918. During the
Battle of Saint-Mihiel
, Pershing commanded the
U.S. First Army
, composed of seven
divisions
and more than 500,000 men, in the largest offensive operation ever undertaken by United States armed forces. This successful offensive was followed by the
Meuse-Argonne offensive
, lasting from September 26 to November 11, 1918, during which Pershing commanded more than one million American and French combatants. In these two military operations, Allied forces recovered more than 200 sq mi (488 km
2
) of French territory from the German army. By the time the
World War I Armistice
had suspended all combat on November 11, 1918, the American Expeditionary Forces had evolved into a modern, combat-tested army.
[1]
Late in the war, American units ultimately fought in two other theaters at the request of the European powers. Pershing sent troops of the
332d Infantry Regiment
to Italy, and President Wilson agreed to send some troops, the
27th
and
339th Infantry Regiments
, to Russia.
[19]
These latter two were known as the
American Expeditionary Force Siberia
,
[20]
and the
American Expeditionary Force North Russia
.
[21]
Using questionnaires filled out by doughboys as they left the Army, Gutièrrez reports that they were not cynical or disillusioned. They fought "for honor, manhood, comrades, and adventure, but especially for duty."
[22]
Casualties
[
edit
]
See also:
General Pershing WWI casualty list
The AEF sustained about 320,000 casualties: 53,402 battle deaths, 63,114 noncombat deaths and 204,000 wounded.
[23]
Relatively few men suffered actual injury from poison gas, although much larger numbers mistakenly thought that they had been exposed.
[19]
The
1918 influenza pandemic
during the fall of 1918 took the lives of more than 25,000 men from the AEF, while another 360,000 became gravely ill.
Demobilization
[
edit
]
After the
Armistice of November 11, 1918
thousands of Americans were sent home and demobilized. On July 27, 1919, the number of soldiers discharged amounted to 3,028,487 members
[24]
of the military, and only 745,845 left in the American Expeditionary Forces